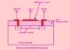
Converting current into voltage involves the use of a device called a resistor. This process is governed by Ohm’s Law, which states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to convert current into voltage:
- Ohm’s Law:
- Ohm’s Law is represented by the equation V = I * R, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance. This law describes the linear relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.
- Series Resistor Connection:
- To convert current into voltage, a resistor is connected in series with the current-carrying path. The voltage across the resistor will be proportional to the current flowing through it, based on Ohm’s Law.
- Voltage Measurement:
- Connect a voltmeter across the resistor to measure the voltage. The voltage measured across the resistor will be directly proportional to the current passing through it.
- Calculating Voltage:
- Using Ohm’s Law, you can calculate the voltage across the resistor by multiplying the current (I) by the resistance (R): V = I * R. This formula quantifies the relationship between the applied current and the resulting voltage.
- Example Circuit:
- Consider a simple circuit where a current source is connected in series with a resistor. The resistor, in this case, serves the purpose of converting the current into a measurable voltage.
- Voltage Output:
- As current flows through the resistor, the voltage across it can be measured using the connected voltmeter. This voltage represents the conversion of current into voltage.
- Load Considerations:
- It’s essential to consider the impact of the resistor on the original circuit. The resistor acts as a load, and the voltage measured across it may affect the overall circuit behavior.
- Application in Sensors:
- Converting current into voltage is commonly used in various sensors. For example, in a current-based sensor, the current is passed through a resistor, and the resulting voltage is measured. This voltage can then be correlated to the original current, providing a voltage representation of the sensed quantity.
- Transimpedance Amplifiers:
- In some cases, operational amplifiers configured as transimpedance amplifiers are used to convert current to voltage. In this configuration, the current flows into the inverting input of the operational amplifier, and the output voltage is proportional to the input current.
- Calibration and Accuracy:
- Ensure that the resistor used is accurately specified to achieve precise voltage conversion. Calibration may be necessary to account for resistor tolerances and variations.
In summary, converting current into voltage involves connecting a resistor in series with the current path and measuring the voltage across the resistor. Ohm’s Law provides the fundamental relationship, and the voltage measured across the resistor represents the converted voltage. This principle is widely used in various applications, including sensors and signal conditioning circuits.