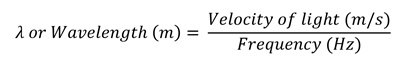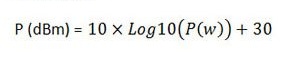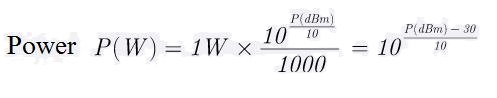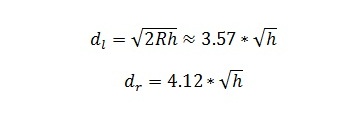Frequency to Wavelength converter
This converter is designed to translate frequency values into corresponding wavelengths, which is crucial in RF, antenna design, and communication systems. Conversion Formula for Wavelength λ = c / f Explanation of the Formula The wavelength (λ) in meters is obtained by dividing the speed of light (c ≈ 299,792,458 m/s) by the frequency (f) … Read more