Types of Electricity
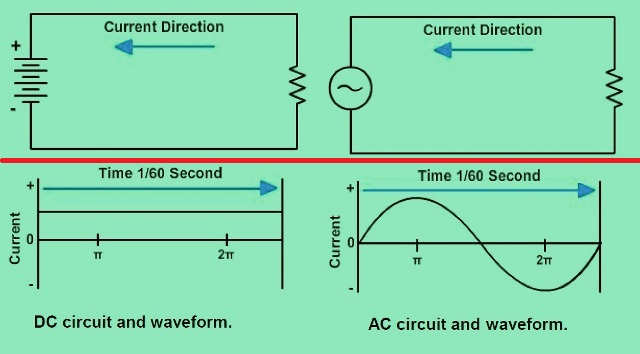
Direct Current
Current flowing in one direction only is called direct current. The letters “DC” Represent direct current. A battery generates direct current. The voltage source behind it This DC current has the same polarity all the time. The current flow is from negative to positive.
Alternating Current
Mostly you work with alternating current. The letters “AC” represent AC. It’s called AC because it changes directions (changes). An AC The cycle consists of a positive and a negative change. AC current flows in one direction for half one cycle then reversed for half a cycle. In the US we use 60 cycles per Second (60 Hertz (Hz).) Since there is one positive and one negative change per second Cycle, 60 Hz alternating current changes direction 120 times per second.
What is electricity ?
Electricity is a type of energy consisting of the movement of electrons between two points when there is a potential difference between them, which can produce what is called an electric current.
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles, such as electrons, through conductive materials. It is a fundamental force of nature that powers our modern world. It is generated through various methods, including burning fossil fuels, harnessing renewable sources like wind and solar, and nuclear reactions.
Once generated, electricity can be transmitted over long distances through power lines and distributed to homes, businesses, and industries for various applications. When harnessed, electricity provides us with the ability to power devices, generate light, operate machinery, and facilitate communication, making it an essential aspect of our daily lives.
There are several types of electricity commonly used and generated in various ways. Here are some of the main types:
1. Direct Current (DC): Direct current is the flow of electric charge in one direction. It has a constant voltage polarity and is typically produced by batteries, fuel cells, and photovoltaic (solar) cells.
2. Alternating Current (AC): Alternating current is the flow of electric charge that periodically reverses direction. AC is the most commonly used form of electricity for power transmission and distribution. It is produced by generators at power plants and used in homes, businesses, and industries.
3. Three-Phase AC: Three-phase AC is a type of alternating current where three separate phases of electricity are generated and distributed. It is commonly used in industrial applications and large-scale power systems due to its ability to provide higher power and efficiency.
4. Low Voltage and High Voltage: Electricity is often categorized into low voltage and high voltage based on the voltage level. Low voltage electricity typically refers to voltages below 1,000 volts, commonly used in residential, commercial, and small-scale industrial applications. High voltage electricity refers to voltages above 1,000 volts and is used in power transmission and large-scale industrial applications.
5. Renewable Electricity: Renewable electricity is generated from renewable energy sources that are naturally replenished, such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass. These sources are considered environmentally friendly and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuel-based electricity generation.
6. Fossil Fuel Electricity: Fossil fuel electricity is generated from non-renewable energy sources such as coal, natural gas, and oil. These fuels are burned to produce heat, which is then used to generate electricity through steam turbines or internal combustion engines.
7. Nuclear Electricity: Nuclear electricity is generated by harnessing the energy released from nuclear reactions, specifically nuclear fission. This involves splitting atoms of heavy elements like uranium or plutonium in a controlled manner to produce heat, which is then converted into electricity.
These are some of the main types of electricity, each with its own characteristics and applications. The choice of electricity type depends on factors such as the intended use, availability of resources, environmental considerations, and efficiency requirements.